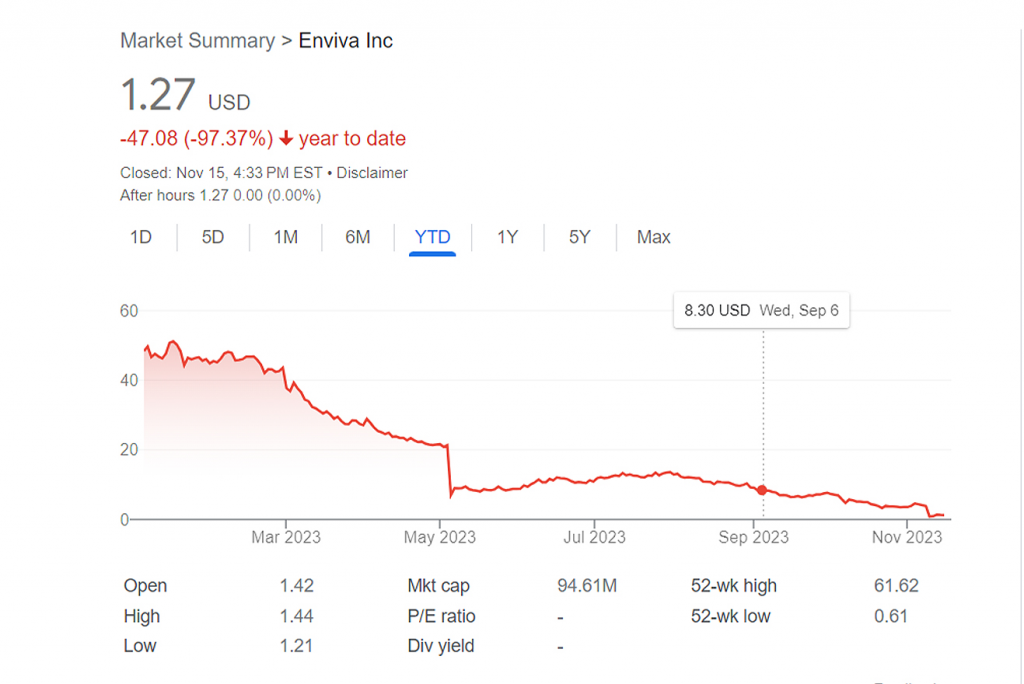
Rachel Donald of Ireland, an environmental journalist par excellence, was recruited to Mongabay in 2023 to take over its nearly decade-old podcast called The Mongabay Newscast. With good reason. She is the heart and soul behind the popular Planet: Critical, which covers the climate crisis by podcast and newsletter with subscribers in 160 countries.
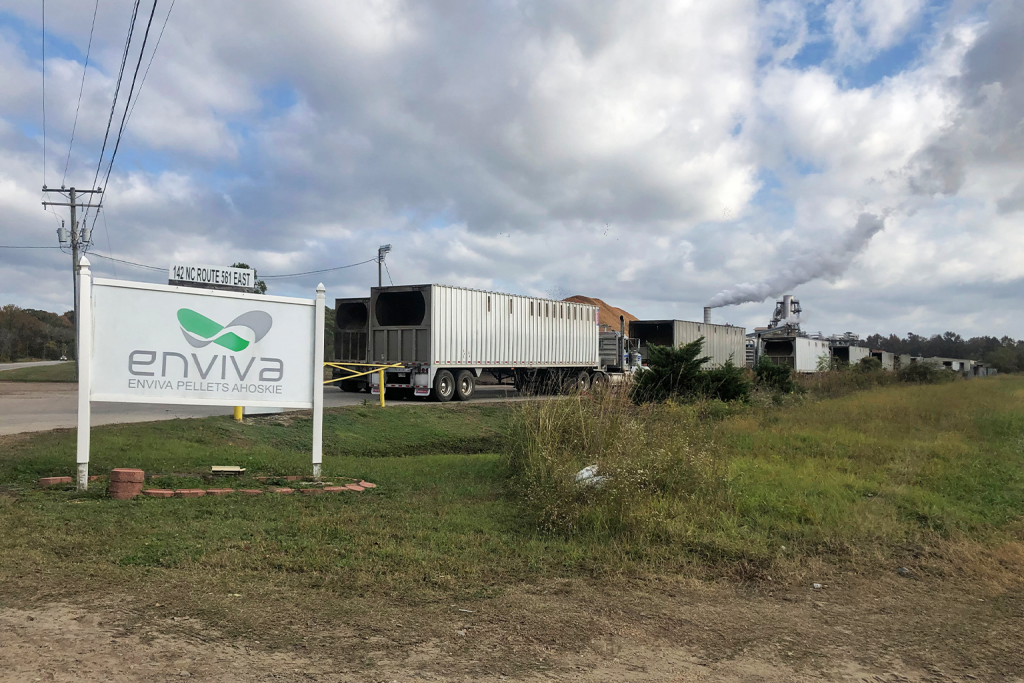
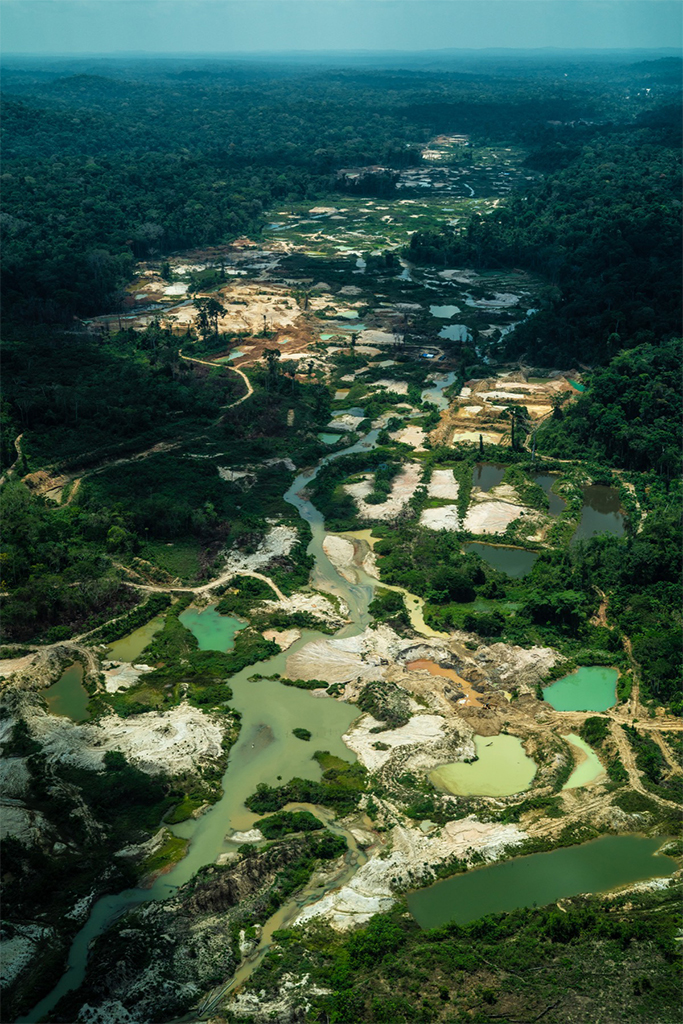
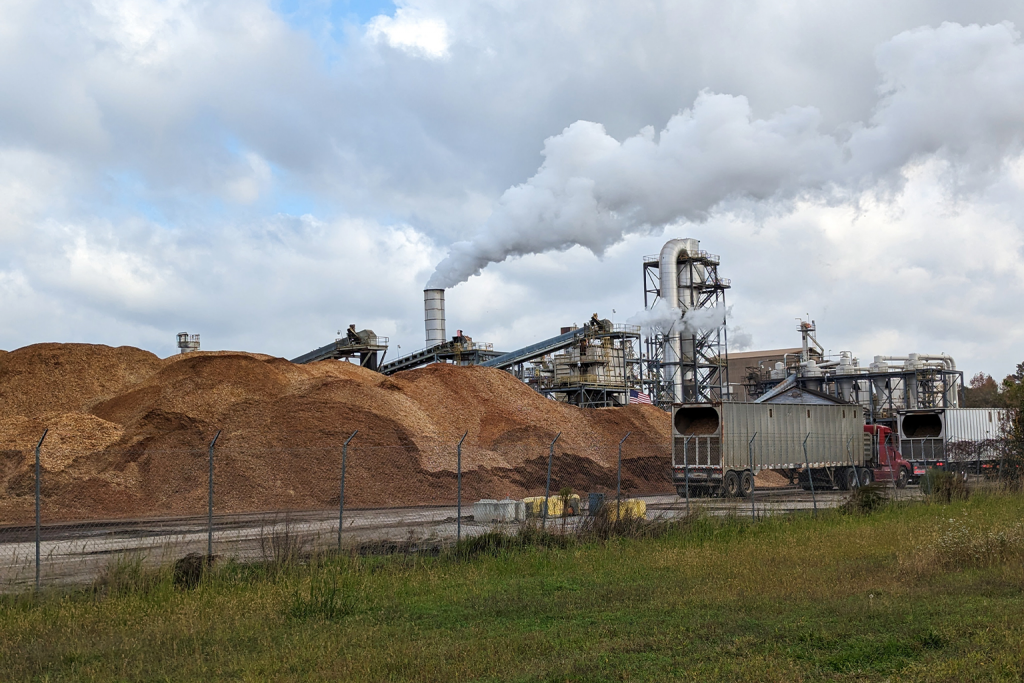
Rachel had been reporting on Drax, the United Kingdom’s largest consumer of forest biomass for energy and a leading wood-pellet producer. She wanted to do a podcast on the issue, with Drax at the center. My colleague Mike DiGirolamo, with whom I’ve recorded from COP26 in Glasgow in 2021 and who works on the podcast, recommended she set up an interview with me. After all, I had just reported on what appears to be Drax’s intention to open the first wood-pellet mills in California.
Here’s the podcast link. I record a lot of these on both sides of the mic. Rachel was easily the best host I’ve been interviewed by. She combines a deep knowledge of the subject matter with a sharp ear for listening, a real plan for the arc of the conversation and a voice that exudes a genuine passion for the subject matter.
As Mike, who edited and produced the podcast from his home in Australia, says at the outset, if you are new to the issues of forest biomass for energy, my discussion with Rachel Donald is a good place to start.