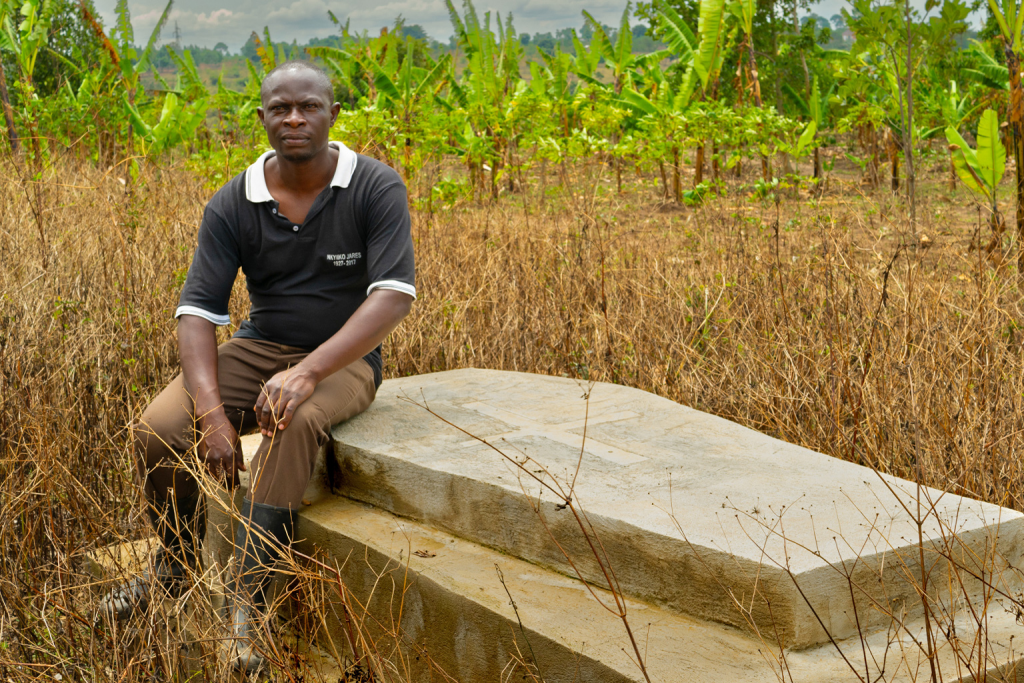
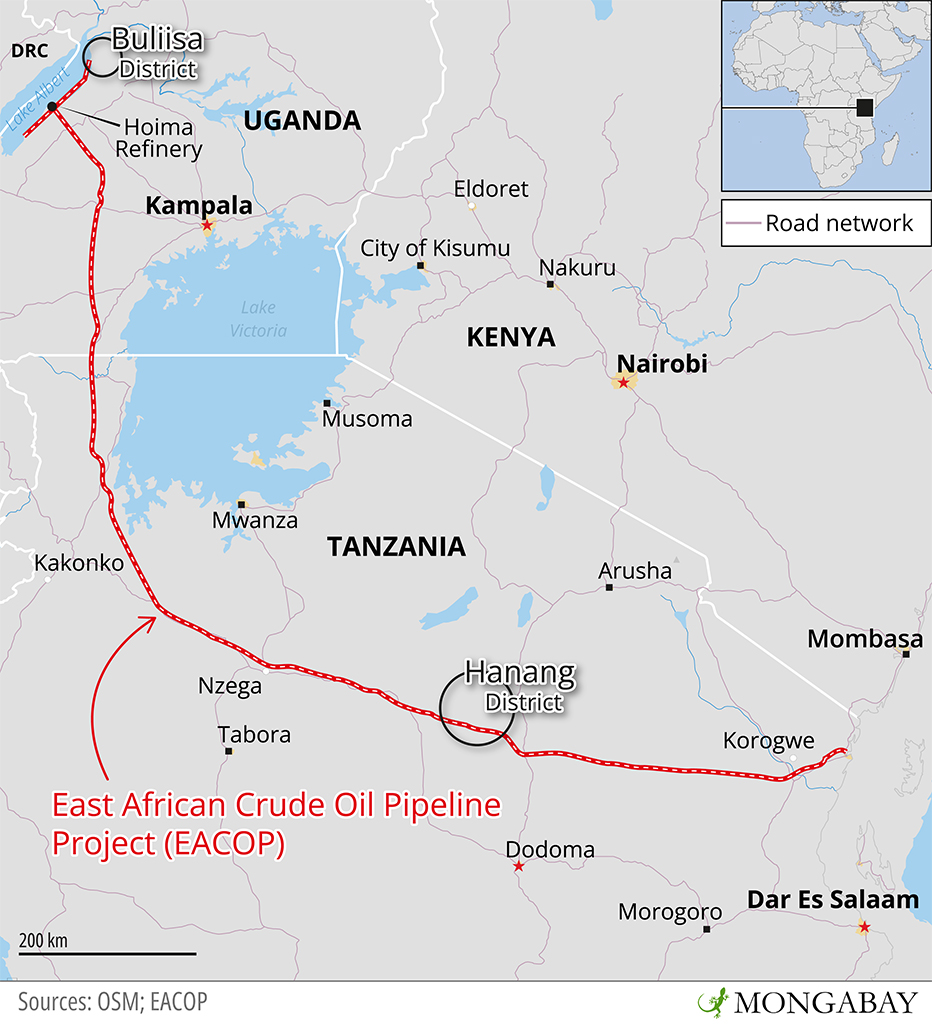
This story here sprung directly from renewing my contact with a trusted source whom I met in December 2015 at the United Nations climate summit in Paris. That source: the Rev. Fletcher Harper, director of GreenFaith, an international faith-based NGO. I interviewed him in October for my recent story about Pope Francis’ latest papal letter in defense of the environment and whether it would reignite climate action by faith leaders around the world. A week after the story ran, Harper asked if I would be interested to covering an investigation GreenFaith was getting prepared to release about the impact on graves and burials sites along the 895-mile long route of the proposed East African Crude Oil Pipeline (EACOP).
My editor forwarded the pitch to Terna Gyuse, a Mongabay editor based in Ghana, who assigned me the story. Because of security concerns, I could not reach out to sources in Africa and Europe prior to GreenFaith’s release of “As If Nothing Is Sacred,” the nine-month investigation’s grim and detailed findings. I was able to pull together what I needed fairly quickly. Even TotalEnergies in France, which GreenFaith accuses of being heedless in disturbing more than 2,000 graves along the pipeline route, responded within hours to questions I had sent. Terna did an excellent job editing the story.