These cut trees, viewed by California biologist and writer Maya Khosla, were harvested recently in Stanislaus National Forest, an area that falls within the potential harvest radius of a proposed wood pellet mill in Tuolumne County in central California. The mature trees were taken as part of a thinning strategy which often includes unburned forests for what is hoped to be wildfire prevention. Photo courtesy of Isis Howard.
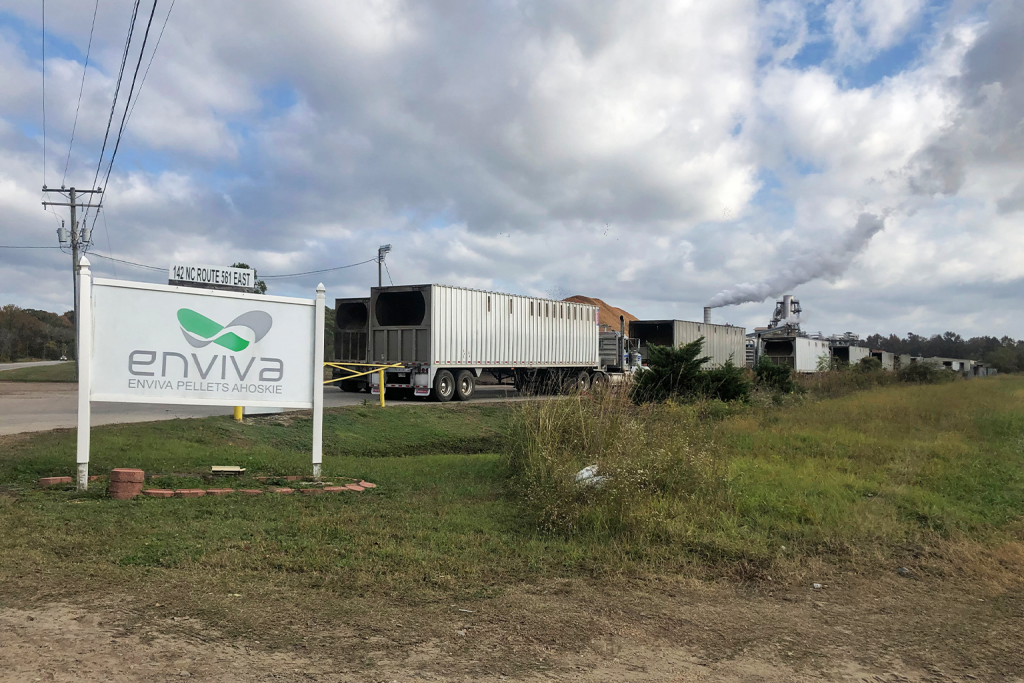
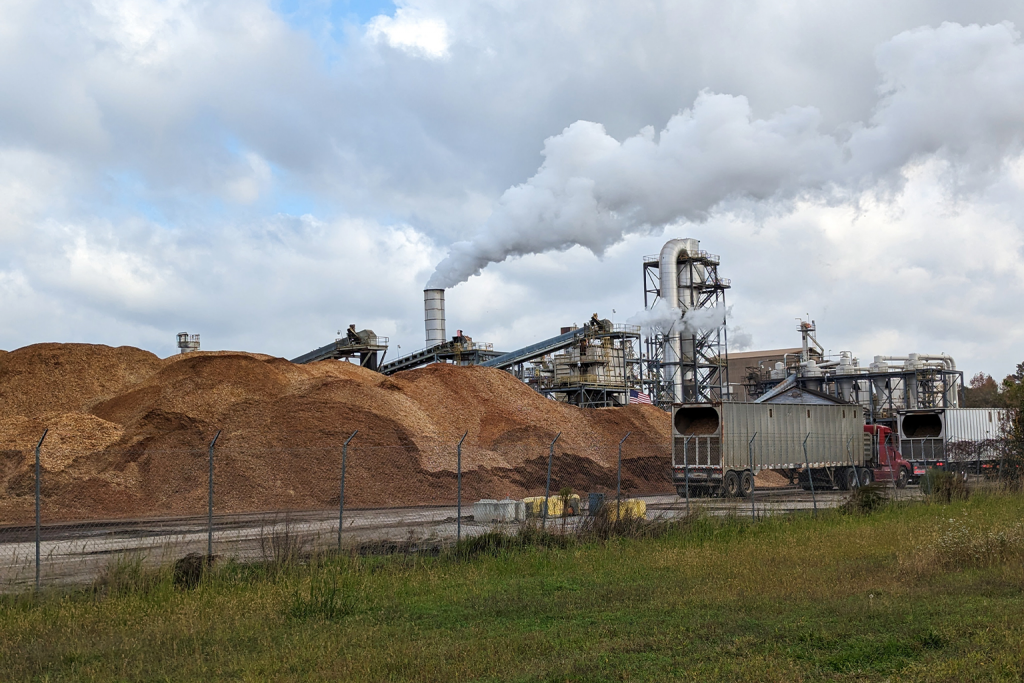
I have been following the developments of the potential for wood pellet manufacturing in California for more than a year. The news hook that Drax, the United Kingdom based energy supplier and pellet maker, had recently entered into an agreement with a California governmental nonprofit that is promoting and planning for two new pellet mills, was what I needed to write this story.
It’s another forest biomass story steeped in controversy, as most of these stories are — whether they are centered in my home state of North Carolina, the US Southeast, or overseas in the European Union, United Kingdom, Japan or South Korea. The twist in California, a state ravaged by climate change-fueled wildfires since 2020, is that the “thinning” of the state’s vast woodlands and collection of burned trees and residues for wood pellet feedstock, will help reduce the risk of wildfires while boosting sagging economies in rural counties that cover parts of eight national forests.
More than 100 environmental groups, Indigenous tribes and community organizations have been pushing back against this growing industry in California and especially against the central argument for its existence — wildfire mitigation. My story explains both sides. There will very likely be more stories to come from California.

As part of its strategy to gather forest wood for wood pellet production, GSNR has said it will promote “salvage logging” in areas damaged or destroyed by wildfire. This June 2022 photo of an area burned in the Dixie Fire, one of the worst ever in California, illustrates what salvage logging looks like. “Ecologically there is nothing worse that can be done to a forest in California than to log after fire,” said Gary Hughes, a forest advocate with Biofuelwatch. “It is likened to beating a burn victim.” Image courtesy of Kimberly Baker/Klamath Forest Alliance.